According to a recent report, the market for healthcare-related wearable technology is estimated to reach $30 billion by 2027, and the volume of healthcare wearables is projected to exceed one trillion by 2022.
Wearable gadgets have progressed from simple mechanical equipment to intelligent mechatronic systems. Smart wearable medical devices aid in the shift from the treatment of acute illness to the practice of preventative care.
However, remote monitoring capabilities will significantly benefit patient care and healthcare administration. This article succinctly examines the uses of wearable medical technologies in everyday practice. Keep reading to learn more now!
8 Regular Instances Where Smart Wearable Medical Devices Are Used in Healthcare
1. The Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Device
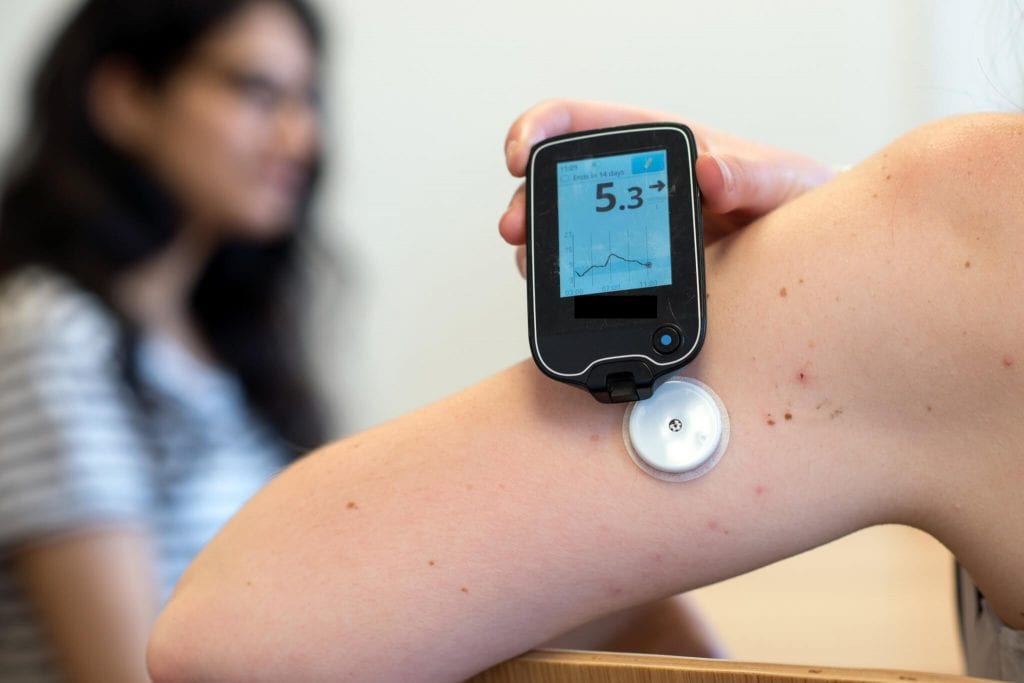
Patients with type 1 diabetes who use CGM (continuous glucose monitoring) sensors can monitor their blood sugar levels and make necessary adjustments. Additionally, this wearable device can benefit patients undergoing intensive insulin therapy, hypoglycemic blindness, or low or high blood insulin levels. Software development, medicine, health sciences, and environmental health specialists may work with this gadget and incorporate its technology.
2. Digital Skin Patching Sensor

The next wave of wearable health technology is electronic skin patches. Wireless transmitters built into the sensors in the sleeves give assigned health personnel constant remote access to information. They are used for motion sensing, drug delivery, wound care, and monitoring vital signs. Practical medical sciences, medical technology, pharmaceuticals, and kinesiology are all areas of study that can lead to the use of these devices.
3. The Photoplethysmography (PPG) Wearable Device

Medical experts can use photoplethysmography gadgets to measure the blood supply to the heart non-invasively. The device monitors circulation and helps explain heart rate variations using a light sensor. PPG wearable sensors are mobile and transmit data when the wearer is moving.
4. Newborn and Pregnancy Wearable Monitoring Device
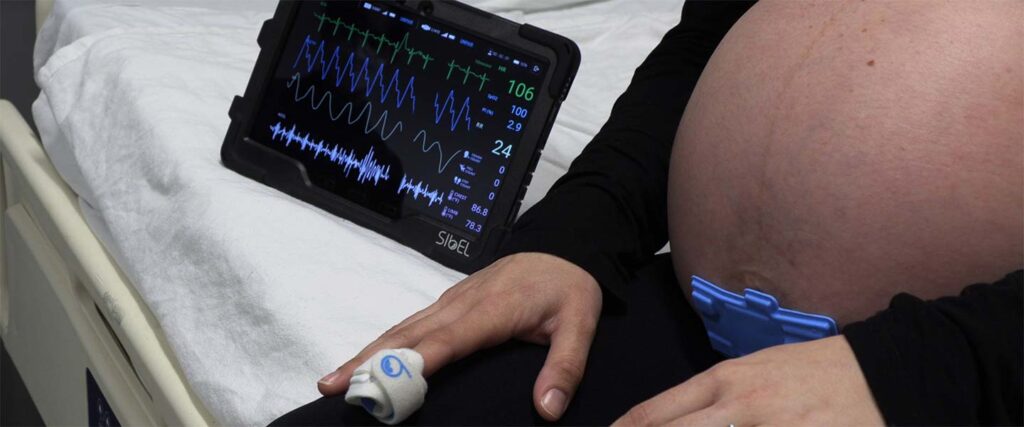
The heartbeat and movements of a developing fetus are continuously monitored using wearable pregnancy detectors. Infant trackers fastened to the foot or ankle transmit real-time data while monitoring respiration, sleep, and movement. Wearable technology is used in obstetrics, nursing, and software development fields.
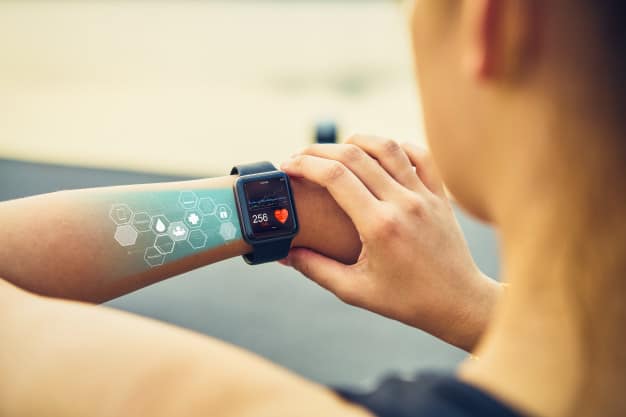
5. Smartwatches

Smartwatches benefit both patients and healthcare practitioners by allowing for the early diagnosis of any concerning symptoms. Devices frequently offer blood oxygen readings, ECG sensors, stress reduction, and heart rate monitoring. Healthcare, fitness and computer-related industry practitioners often use this unique wearable device.
6. Head-wearable Displays and Smart Glasses
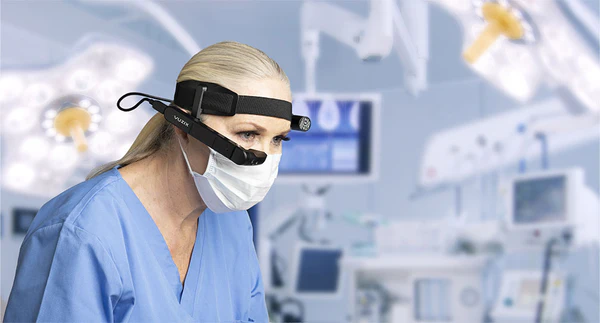
People with visual loss and disabilities increasingly use smart glasses (virtual reality and augmented reality glasses) to help them. They are used by optometrists, psychologists, opticians, and other professionals to enhance patients’ quality of life in several ways. Devices can have zoom, opacity, or voice style controls to help fix or improve eyesight.
7. Intelligent Contact Lenses
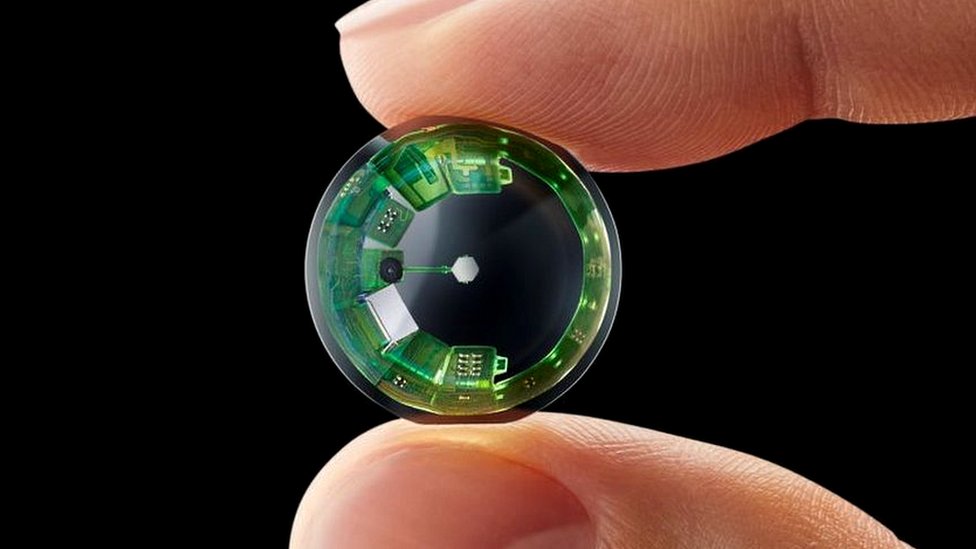
Optometrists use intelligent contact lenses to monitor eye wellness and spot eye disorders earlier. Images are enlarged using augmented reality devices and projected onto smartphones for better sight. Optometrists, bioscientists, and nurses will most likely employ them in their work.
8. Smart Wearable Wound Care Gadget
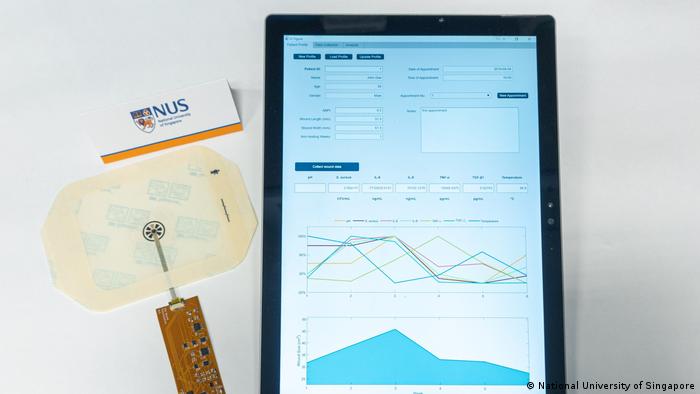
They are accommodating to people with chronic illnesses that cause open wounds to remain. Wound care specialists use them to promote better outcomes and reduce the need for amputations due to non-healing damage. They are used by those in engineering, functional medicine, and applied health sciences.
Read Also
- The Role of Ingredients in Your Skincare: What to Look ForSkincare works best when you understand what goes into the products you use daily. Ingredients form the foundation of every formula and determine how the skin reacts over time. Each cream, cleanser, or serum has its own role, determined by its ingredients. Learning what to look for helps you pick products that help skin and… Read more: The Role of Ingredients in Your Skincare: What to Look For
- Your Guide to Finding a Trusted DentistChoosing the right dentist in Sandgate or your area is crucial for maintaining good oral health and achieving a confident smile. With countless dental practices to choose from, patients may find the task daunting. Data from the American Dental Association indicates that there are over 200,000 practicing dentists in the United States, highlighting the importance… Read more: Your Guide to Finding a Trusted Dentist
- Achieving a Defined, Balanced Facial Contour in SingaporeA well-defined jawline and a gently tapered lower face — commonly referred to as a V-shaped face — is a look many people aspire to. In Singapore’s beauty and aesthetic scene, treatments that help refine facial contours have grown in popularity as more individuals seek subtle, natural enhancements that boost confidence and balance facial features.… Read more: Achieving a Defined, Balanced Facial Contour in Singapore
- The Wellness Blueprint: How Your DNA Holds the AnswerGenetic testing is revolutionizing preventive healthcare by offering insights into individual health risks. By analyzing DNA, these tests provide a personalized health blueprint that can guide lifestyle and medical decisions. This approach, often referred to as DNA wellness testing, helps to optimize health naturally and prevent potential diseases. In recent years, genetic testing has become… Read more: The Wellness Blueprint: How Your DNA Holds the Answer
- Exploring the Benefits of Infusion Therapy in OKC: The Ultimate GuideUnderstanding Infusion Therapy: A Deep Dive into Its Purpose and Process What exactly is Infusion Therapy? Infusion therapy is an advanced medical treatment that delivers medication and nutrients directly into the bloodstream through a vein, typically via an IV (intravenous) line. This method is particularly beneficial for patients who require a concentrated dose of medication,… Read more: Exploring the Benefits of Infusion Therapy in OKC: The Ultimate Guide
Education and Professions in the Field of Wearable Medical Technology
The medical field is expansive, and many certifications and professions integrate with wearable medical tech. From public health caregivers to therapists, most medical careers utilize some form of wearable technology application. Here are some top healthcare careers at the forefront of wearable medical technology:
1. Health Science
Health science is one outstanding field using medical wearables the most. Students and aspirators in the field can find careers within the broad scope of the healthcare industry. Future doctors or business leaders tackle therapeutic services, biotechnology research, and health informatics. Depending on your preference, you can find both in-person and online health science degrees.
2. Audiology
From diagnosis to treatment, audiologists address hearing and ear problems. Both in the clinic and the lab, it is used to make hearing aids more effective, practical, and comfortable in the clinic and the lab. However, compared to hearing aids of the past, which were bulky and didn’t work correctly, today’s smart wearable gadgets are amazing. Possible careers in audiology span research, design, and sales of health wearables.
3. Therapists
Occupational therapists and their aides use commonplace activities to treat patients who are injured, ill, or incapacitated—facilitating patient treatment, which also includes the use of specialized medical equipment. There are good uses for wearable technology in occupational therapy, such as dehydration detectors and ECG trackers. Professionals in this field frequently instruct patients and caregivers on wearable medical technology.
4. Kinesiology
Kinesiologists study the body’s movements, and academic degrees exist at all levels, from associate to doctoral degrees. However, graduates work as fitness trainers, physiotherapists, and exercise physiologists. Online exercise science degrees can build on what you know about kinesiology and give you more freedom to study.
5. Nursing
Nurses frequently come into contact with wearable health devices. Practical nurses are comfortable using wearable medical tech. Registered Nurse schools, other nursing degrees, and both conventional and digital RN courses provide an opportunity to learn much about the wearable health technology industry.
6. Pharmacy
Apart from doctors, pharmacists and pharmacy technicians frequently serve as medical consultants. Professional pharmacists offer advice on wearable technology and explain medical administration and use.
Conclusion
Now you know that smart health monitoring devices’ primary effect on the healthcare system is to simplify existing procedures. The IoT and AI technologies enable medical professionals to conduct constant and real-time patient monitoring. To learn more about the benefits, check the article on wearable health monitoring devices from Epam Anywhere.
Smart wearable medical devices may communicate with users, assigned medical professionals, or other smart devices for data storage or analysis purposes. However, these devices you wear can track even the most minor changes in the body and give you all the information you need to act if you need to.






